Microsoft files patent for smart eyeglasses to measure blood pressure
Glabella continuously records the stream of reflected light intensities from blood flow as well as inertial measurements of the user’s head to come up with blood pressure value.
Microsoft has filed a patent for an eyeglass monitor which is capable of tracking blood pressure that is commonly known as Glabella. The eyeglass is said to be more accurate compared to traditional inflatable cuff. This is being seen as a major improvement in the health sector because they will replace the traditional cuff monitor that specialist uses to track blood pressure which is not very accurate.
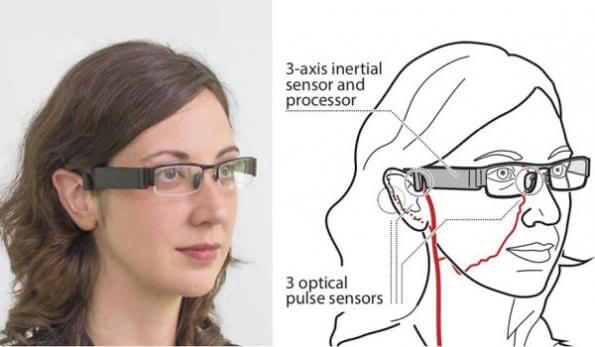
According to Microsoft, the glasses have sensors which are built into the frame and are able to take pulse wave readings from three different area of the face.
The devices are said to measure pulse waves regularly and then store the information, it measures pulse transit time if there were any delays when the blood was being ejected from the heart. It measures the short term behaviours of blood pressure in a patient which Microsoft is saying it shows a significant evaluation of correlation within the patient’s blood pressure.
The sensor is able to serve as a socially-acceptable capture device and it will show no change of behaviour during regular activities and will still; continue collecting the needed information that will inform patients and specialists.
The emerging technologies are now viewed as the game changer and this patent glass has been seen as rivals between Apple, Samsung, Amazon, and Google. These four companies have already filed numerous patents that give clue on how to break ground when it comes to technology in the health sector. Google had Previously filed a patent for eyeglasses which is also for monitoring heart rate.
“Our glasses prototype incorporates optical sensors, processing, storage, and communication components, all integrated into the frame to passively collect physiological data about the user without the need for any interaction,” Holz and Wang wrote on the Microsoft website. “They noted that Glabella also continuously records the stream of reflected light intensities from blood flow as well as inertial measurements of the user’s head. From the temporal differences in pulse events across the sensors, our prototype derives the wearer’s pulse transit time on a beat-to-beat basis.”
“This enables our cuff-less prototype to model the beat-to-beat fluctuations in the user’s blood pressure over the course of the day,” wrote the researchers.
And it can also record its short-term responses to events, such as postural changes, exercise, eating and drinking, resting, medication intake, location changes, or time of day.
This wearable device will really be of great help to patients who require regular blood pressure check-ups. The eyeglasses will be more accurate than the inflatable cuff which is fitted on the wrist to measure blood in the arteries where the blood is narrower and not as deep as the blood under the skin. The researchers are said to conduct real-world trial which showed that this type of technology is more accurate.
Image credit: www.microsoft.com